
“How healthy is my company? Are we adequately prepared to confront market threats and seize market opportunities? Are we doing enough to protect our core business? Do we have a pipeline of businesses to scale? Are we planting seeds for future growth?” CEOs and business leaders often contemplate these questions, yet they typically find themselves immersed in the demanding realm of daily management.
In fact, it is common for business leaders to become so preoccupied with managing daily activities that they forget to consider how the evolving world around them will impact their core business in the future and think about the core business of tomorrow.
This lack of foresight can hinder their companies’ ability to adapt and thrive in the long run. Even if they were initially successful and thrived for some time, they may eventually decline and fade into obscurity. Especially in today’s fast-paced business world, maintaining a competitive advantage and continuously seeking out new growth opportunities are essential. However, with numerous demands vying for attention, finding balance can be challenging. This is where the Three Horizons of Growth framework comes into play.
Introduced by Baghai, Coley, and White in their 1999 book The Alchemy of Growth,[i] the Three Horizons of Growth framework supports businesses in conceptualizing the stages of business maturity and defining strategic priorities to both defend their core business and establish the foundation for long-term growth.
Each horizon represents a distinctive focus of the organization, but together they provide the foundation for a healthy and sustainable business. Each horizon has unique management challenges that leaders have to face. Let’s explore each one separately.
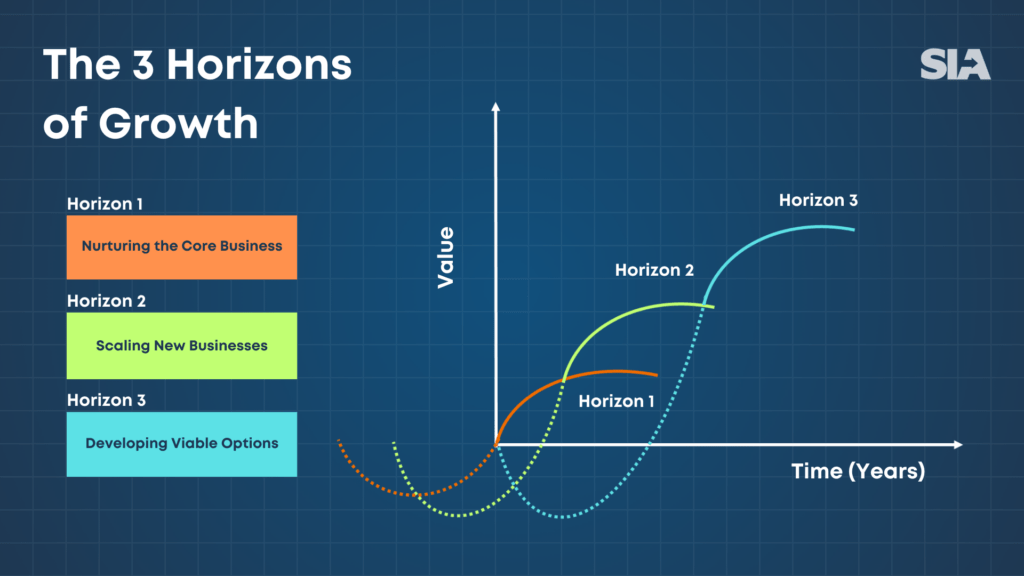
Horizon 1: Nurturing the Core Business
Horizon 1 is dedicated to nurturing the core business of the company. “Core business” refers to the primary activities or operations that a company engages in, typically encompassing its key products or services and the primary markets it serves. As the primary area of expertise, this horizon is crucial for most businesses as it generates the majority of their revenue and profits. However, it is also the most susceptible to disruption from competitors or market changes.
To maintain a competitive advantage, businesses must continually innovate and enhance both their existing products and services, as well as their operational processes. This may involve investing in new technology, streamlining operations to improve margins, or launching product extensions. The objective should be to maximize the untapped potential within those businesses and achieve strong short-term performance to accumulate sufficient resources for funding Horizon 2 and Horizon 3 ventures.
Horizon 2: Scaling New Businesses
Horizon 2 involves developing new revenue streams by scaling new growth opportunities and taking calculated risks. This may entail entering new competitive arenas, developing entirely new products or services, or acquiring to then scale new businesses.
Businesses within this horizon already have some customers and revenue, in other words, they have achieved customer-solution fit and they are showing traction towards product-market fit. While substantial profits may be a few years away, they exhibit promising potential to the extent that they are expected to significantly complement and ultimately even replace the company’s core business. However, achieving this requires significant investments to accelerate business expansion. Unlike in Horizon 1, the focus is on increasing revenue and market share with the aim of reaching profit-market fit.[ii]
Companies must have a handful of Horizon 2 businesses in the pipeline, actively working to transform promising opportunities into future core profit generators. It’s important to carefully select an optimal number, avoiding too many, because Horizon 2 businesses are resource-intensive in terms of both leadership dedication and capital. Failure to have Horizon 2 businesses means that once their core business loses momentum, companies will not have any other businesses to replace it with.
Horizon 3: Developing Viable Options
Horizon 3 focuses on preparing for the long term. It entails making “small bets” on opportunities that, if successful, could eventually achieve the profitability level of Horizon 1. These small bets may involve investing in research projects, acquiring minority stakes in promising ventures, or developing a culture of experimentation. An iconic example of the latter is the one at W. L. Gore & Associates, where all the employees can explore and pursue opportunities within defined boundaries.[iii] However, Horizon 3 bets must be tangible activities and investments, not merely ideas on a whiteboard.
Through Horizon 3 bets, companies should ensure they are actively pursuing the option to enter the game without overcommitting resources, possibly bridging the gap between their current capabilities and those required for future success, and fostering a growth mindset.
Business leaders should understand that they need to make numerous Horizon 3 bets since most of them will fail. Moreover, those that do succeed may take several years to materialize, as they progress from Horizon 3 to Horizon 2, and eventually to Horizon 1. Importantly, they should not hesitate to eliminate bets that fail to meet expectations. However, they should continue to actively pursue Horizon 3 opportunities because failing to do so risks hindering their companies’ long-term growth prospects.
By balancing short-term considerations with long-term objectives, the Three Horizons of Growth can empower businesses to achieve sustainable growth. This framework offers companies a structured approach to maintaining a competitive advantage through continuous innovation and enhancement of products and processes, thus equipping them to navigate future challenges and seize opportunities.
In the journey of strategy formulation, the Three Horizons of Growth framework plays a crucial role in determining strategic priorities. By categorizing these priorities into three distinct horizons, business leaders can ensure effective attention to both the present and future success of their business.
A word of caution is warranted here, though. Merely because the horizons are labeled with progressive numbers does not imply that companies should address them sequentially. The three horizons should not be confused with short, medium, and long-term planning. Rather, business leaders must manage businesses across all three horizons simultaneously.
Strategic priorities spanning the three horizons, along with the initiatives and resources allocated to realize each priority, must be defined in parallel. The numerical sequence denotes instead that initiatives within the three horizons will yield results over different time frames. Over time, successful ventures may transition from Horizon 2 to Horizon 1 or from Horizon 3 to Horizon 2.
Business leaders can follow these steps to unleash the power of the Three Horizons of Growth framework.
Step 1: Identify Strategic Priorities
The first step is to identify the company’s strategic priorities. To do this, defining the company’s vision and mission and conducting thorough internal and external analyses are crucial. Robust strategic priorities are those that leverage the company’s strengths and weaknesses to address its opportunities and threats. (Learn more about strategic priorities.)
Step 2: Divide Strategic Priorities into Three Horizons
Following the identification of strategic priorities, business leaders should categorize them into the three horizons. Priorities focused on core business operations belong to Horizon 1, while those targeting emerging scaling opportunities and future growth belong to Horizon 2 and Horizon 3, respectively. It is important to remember that these priorities may yield results within the next 12-18 months if they’re in Horizon 1, within 2 or 3 years if they’re in Horizon 2, and later if they’re in Horizon 3. However, all priorities should be pursued simultaneously.
Step 3: Allocate Resources Accordingly
Once business leaders have identified robust strategic priorities and divided them into the three horizons, they should focus on allocating resources appropriately. It is important to note that “resources” don’t solely refer to budget, in terms of both operating expenses and capital expenditure. An often underestimated aspect is that the type of talent and leadership time needed to successfully manage the three horizons differs.
Due to the nature of Horizon 1, individuals with a profound understanding of the business, as well as the discipline and expertise to improve efficiency and achieve targets, are required. On the other hand, Horizon 2 businesses demand individuals with a strong entrepreneurial drive and sharp decision-making skills, who are comfortable dealing with ambiguity and change.
Finally, Horizon 3 ventures demand unconventional thinkers—individuals who can break free from established patterns and leverage their intellectual freedom, creativity, and curiosity to uncover new opportunities. Using the terminology of Baghai, Coley, and White, Horizon 1 needs “operators”, Horizon 2 needs “business builders”, and Horizon 3 needs “visionaries.”
Step 4: Regularly Review and Adjust
The Three Horizons of Growth is not a one-time exercise. It is essential to regularly review and adjust business strategies as the market evolves. This may involve reallocating resources from one horizon to another or seizing new opportunities as they arise.
Just as with talent, the approach to assessing performance varies across the three horizons. Given that Horizon 1 prioritizes short-term bottom-line results and cash flow, performance metrics may encompass net income growth, productivity improvement rates, and return on invested capital.
Horizon 2 being centered on top-line growth and expanding market share, performance metrics such as revenue growth, market share, and new customer acquisition should be prioritized to enable a realistic assessment of a business’s potential.
As Horizon 3 revolves around making small bets on potential future opportunities, it would be counterproductive to assess their performance solely through traditional financial measures. Instead, it would be more sensible to define initiatives and project-based milestones, such as successfully completing a pilot or securing a partnership.
The Three Horizons of Growth framework has been successfully implemented by numerous companies. One notable example is Amazon.
Amazon initially derived its primary source of revenue from its e-commerce platform, which featured an extensive range of products. In its Horizon 2, the company diversified beyond e-commerce, venturing into areas such as Amazon Web Services (cloud computing) and Amazon Prime Video (streaming services), both of which have since become significant revenue streams. It’s worth noting that both businesses initially started as Horizon 3 bets.
Horizon 3 involves Amazon’s ongoing investment in emerging technologies and areas with potential for future growth. This includes ventures into artificial intelligence (AI) for various applications, such as enhancing customer experience and optimizing logistics, as well as initiatives like drone delivery for faster and more efficient shipping.
A classic example, as provided by Baghai, Coley, and White, addresses the question of how The Walt Disney Company (Disney) sustained growth for so long. Building on its expertise in the animation industry, the company pursued initiatives in all the three horizons.
In Horizon 1, Disney concentrated on theme parks, vacation resorts, and live experiences. Transitioning to Horizon 2, the company expanded into film studios and media networks. Horizon 3 involved venturing into new distribution concepts and technologies to adapt to evolving consumer preferences and technological advancements.

In conclusion, the Three Horizons of Growth framework is a powerful tool that leaders can adopt to ensure the long-term sustainability of their companies. As articulated by Baghai, Coley, and White, “the fact that a company’s business blossoms and then fades does not mean that the company must die.” Companies can and should continually reinvent themselves, replacing fading businesses with new, robust ones. This continuous process of business creation will enable companies to ensure sustainable growth and continue on a truly successful journey.
[i] Mehrdad Baghai, Stephen Coley, and David White, The Alchemy of Growth: Practical Insights for Building the Enduring Enterprise (Reading, Massachusetts: Perseus Books, 1999)Davide Sola and Jérôme Couturier, How to Think Strategically: Your Roadmap to Innovation and Results (Harlow, England; New York: Pearson, 2014).
“Enduring Ideas: The three horizons of growth,” McKinsey Quarterly, December 1, 2009, https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/strategy-and-corporate-finance/our-insights/enduring-ideas-the-three-horizons-of-growth#, accessed April 2024.
[ii] Jeffrey F. Rayport, Davide Sola, and Martin Kupp, “The Overlooked Key to a Successful Scale-Up,” Harvard Business Review, January-February 2023, https://hbr.org/2023/01/the-overlooked-key-to-a-successful-scale-up, accessed April 2024.
[iii] Davide Sola, “Success Is the Mirror of Effort: Adopting a Growth Mindset in Strategy Formulation and Execution,” Strategy in Action, https://strategyinaction.io/success_is_a_mirror_effort_growthmindset/, accessed April 2024.